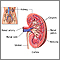
Distal renal tubular acidosis is a disease that occurs when the kidneys do not properly remove acids from the blood into the urine. As a result, too much acid remains in the blood (called acidosis).
Causes
When the body performs its normal functions, it produces acid. If this acid is not removed or neutralized, the blood becomes too acidic. This can lead to electrolyte imbalances in the blood. It can also cause problems with normal function of some cells.
The kidneys help control the body's acid level by removing acid from the blood and excreting it into the urine.
Distal renal tubular acidosis (type I RTA) is caused by a defect in the kidney tubes that causes acid to build up in the blood.
Type I RTA is caused by a variety of conditions, including:
- Amyloidosis, a buildup of abnormal protein, called amyloid, in the tissues and organs
- Fabry disease, an abnormal buildup in the body of a certain type of fatty substance
- High level of calcium in the blood
- Sickle cell disease, red blood cells that are normally shaped like a disk take on a sickle or crescent shape
- Sjögren syndrome, an autoimmune disorder in which the glands that produce tears and saliva are destroyed
- Systemic lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue
- Wilson disease, an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues
- Use of certain medicines, such as amphotericin B, lithium, and analgesics
Symptoms
Symptoms of distal renal tubular acidosis include any of the following:
- Confusion or decreased alertness
- Fatigue
- Impaired growth in children
- Increased breathing rate
- Kidney stones
- Nephrocalcinosis (too much calcium deposited in the kidneys)
- Osteomalacia (softening of the bones)
- Muscle weakness
Other symptoms may include:
- Bone pain
- Decreased urine output
- Increased heart rate or irregular heartbeat
- Muscle cramps
- Pain in the back, flank, or abdomen
- Skeletal abnormalities
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms.
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Arterial blood gas
- Blood chemistry
- Urine pH and acid loading test
- Bicarbonate infusion test
- Urinalysis
Calcium deposits in the kidneys and kidney stones may be seen on:
- X-rays
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
Treatment
The goal is to restore normal acid level and electrolyte balance in the body. This will help correct bone disorders and reduce calcium buildup in the kidneys (nephrocalcinosis) and kidney stones.
The underlying cause of distal renal tubular acidosis should be corrected if it can be identified.
Medicines that may be prescribed include potassium citrate, sodium bicarbonate, and thiazide diuretics. These are alkaline medicines that help correct the acidic condition of the body. Sodium bicarbonate may correct the loss of potassium and calcium.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The disorder must be treated to reduce its effects and complications, which can be permanent or life threatening. Most people get better with treatment.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of distal renal tubular acidosis.
Get medical help right away if you develop emergency symptoms such as:
Prevention
There is no prevention for this disorder.
Alternative Names
Renal tubular acidosis - distal; Renal tubular acidosis type I; Type I RTA; RTA - distal; Classical RTA
References
Bushinsky DA. Kidney stones. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 32.
Dixon BP. Renal tubular acidosis. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 569.
Seifter JL. Acid-base disorders. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 104.
Review Date 12/31/2023
Updated by: Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.