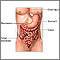
Stools that are pale, clay, or putty-colored may be due to problems in the biliary system. The biliary system is the drainage system of the gallbladder, liver, and pancreas.
Considerations
The liver releases bile salts into the stool, giving it a normal brown color. You may have clay-colored stools if you have a liver infection that reduces bile production, or if the flow of bile out of the liver is blocked.
Yellow skin (jaundice) often occurs with clay-colored stools. This may be due to the buildup of bile chemicals in the body.
Dark urine also may occur with clay-colored stools.
Causes
Possible causes for clay-colored stools include:
- Alcoholic hepatitis
- Biliary cirrhosis
- Cancer or noncancerous (benign) tumors of the liver, biliary system, or pancreas
- Cysts of the bile ducts
- Gallstones
- Some medicines
- Narrowing of the bile ducts (biliary strictures)
- Sclerosing cholangitis
- Structural problems in the biliary system that are present from birth (congenital)
- Viral hepatitis
There are other less common causes not listed here.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if your stools are not the normal brown color for several days.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam. They will ask questions about your medical history and symptoms. Questions may include:
- When did the symptom first occur?
- Is every stool discolored?
- What medicines do you take?
- What other symptoms do you have?
Tests that may be done include:
- Blood tests, including tests to check liver function and for viruses that might affect the liver
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Imaging studies, such as an abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI of liver and bile ducts
Images
References
Korenblat KM. Approach to the patient with jaundice or abnormal liver tests. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 133.
Lidofsky SD. Jaundice. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 21.
Squires JE, Balistreri WF. Manifestations of liver disease. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 403.
Review Date 8/12/2024
Updated by: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Gastroenterologist, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.