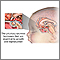
A pituitary tumor is an abnormal growth in the pituitary gland. The pituitary is a small gland at the base of the brain. It regulates the body's balance of many hormones.
Causes
Most pituitary tumors are noncancerous (benign). Up to 10% to 20% of people have pituitary tumors. Many of these tumors do not cause symptoms and are never diagnosed during the person's lifetime.
The pituitary is part of the endocrine system. The pituitary helps regulate the release of hormones from other endocrine glands, such as the thyroid, sex glands (testes or ovaries), and adrenal glands. The pituitary also releases hormones that directly affect body tissues, such as bones and the breast milk glands. The pituitary hormones include:
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
- Growth hormone (GH)
- Prolactin
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
 Watch this video about:Pituitary gland
Watch this video about:Pituitary glandAs a pituitary tumor grows, the normal hormone-releasing cells of the pituitary may be damaged. This results in the pituitary gland not producing enough of some or all of its hormones. This condition is called hypopituitarism.
The causes of pituitary tumors are unknown. Some tumors are caused by hereditary disorders such as multiple endocrine neoplasia I (MEN I).
The pituitary gland can be affected by other brain tumors that develop in the same part of the brain (skull base), resulting in similar symptoms.
Symptoms
Some pituitary tumors produce too much of one or more hormones. As a result, symptoms of one or more of the following conditions can occur:
- Hyperthyroidism (thyroid gland makes too much of its hormones; this is an extremely rare condition of pituitary tumors)
- Cushing syndrome (body has a higher than normal level of the hormone cortisol)
- Gigantism (abnormal growth due to higher than normal level of growth hormone during childhood) or acromegaly (higher than normal level of growth hormone in adults)
- Nipple discharge and irregular or absent menstrual periods in women due to excess of the hormone prolactin
- Decreased sexual function in men due to excess of the hormone prolactin
Symptoms caused by pressure from a larger pituitary tumor may include:
- Changes in vision such as double vision, visual field loss (loss of peripheral vision), drooping eyelids or changes in color vision.
- Headache.
- Lack of energy.
- Nasal drainage of clear, salty fluid.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Problems with the sense of smell.
- In rare cases, these symptoms occur suddenly and can be severe (pituitary apoplexy).
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam. Your provider will note any problems with double vision and visual fields, such as a loss of side (peripheral) vision or the ability to see in certain areas.
The exam will check for signs of too much cortisol (Cushing syndrome), too much growth hormone (acromegaly), or too much prolactin (prolactinoma).
Tests to check endocrine function may be ordered, including:
- Cortisol levels -- dexamethasone suppression test, urine cortisol test, salivary cortisol test
- FSH level
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) level
- LH level
- Prolactin level
- Testosterone/estradiol levels
- Thyroid hormone levels -- free T4 test, TSH test
Tests that help confirm the diagnosis include the following:
Treatment
Surgery to remove the tumor is often needed, especially if the tumor is pressing on the nerves that control vision (optic nerves).
Most of the time, pituitary tumors can be surgically removed through the nose and sinuses (transsphenoidal). If the tumor cannot be removed this way, it is removed through the skull.
Radiation therapy may be used to shrink the tumor in people who cannot have surgery. It may also be used if the tumor returns after surgery.
In some cases, medicines are prescribed to shrink certain types of tumors.
Small tumors found incidentally during an MRI for other symptoms can often be followed with repeat MRI imaging over time if they are not causing any hormonal abnormality. Many of these tumors do not grow.
Support Groups
More information and support for people with pituitary tumors and their families can be found at:
- National Cancer Institute -- www.cancer.gov/types/pituitary
- Pituitary Network Association -- pituitary.org
Outlook (Prognosis)
If the tumor can be surgically removed, the outlook is fair to good, depending on whether the entire tumor is removed.
Possible Complications
The most serious complication is blindness. This can occur if the optic nerve is seriously damaged.
The tumor or its removal may cause lifelong hormone imbalances. The affected hormones may need to be replaced, and you may need to take medicine for the rest of your life.
Tumors and surgery can sometimes damage the posterior pituitary (back part of the gland). This can lead to diabetes insipidus, a condition with symptoms of frequent urination and extreme thirst.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop any symptoms of a pituitary tumor.
Alternative Names
Tumor - pituitary; Pituitary adenoma
Images
References
Dorsey JF, Salinas RD, Dang M, et al. Cancer of the central nervous system. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 63.
Melmed S, Casanueva FF. Pituitary adenomas and masses. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 7.
Weiss RE. Anterior pituitary. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 205.
Review Date 4/24/2025
Updated by: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.