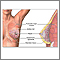
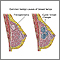
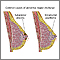
A mammogram is an x-ray picture of the breasts. It is used to evaluate some breast symptoms and to find breast cancer in women with no symptoms (called screening for breast cancer).
How the Test is Performed
You will be asked to undress from the waist up. You will be given a gown to wear. Depending on the type of equipment used and your physical condition, you will sit or stand.
One breast at a time is rested on a flat surface that contains the x-ray plate. A device called a compressor will be pressed firmly against your breast to help flatten the breast tissue. This enables the radiologist to make a better evaluation of your breasts.
The x-ray pictures are taken from several angles. You may be asked to hold your breath as each picture is taken.
You may be asked to come back at a later date to do more mammogram images. This does not always mean you have breast cancer. Your health care provider may simply need to recheck an area that could not be clearly seen on the first test.
TYPES OF MAMMOGRAPHY
Traditional mammography uses film, similar to other x-rays.
Digital mammography is the most common technique:
- It is now used in most breast imaging centers.
- It allows the x-ray image of the breast to be viewed and manipulated on a computer screen.
- It may be more accurate in younger women with dense breasts. It has not yet been proven to help reduce a woman's risk of dying of breast cancer compared to film mammography.
Three-dimensional (3D) mammography (breast tomosynthesis) is a type of digital mammography.
How to Prepare for the Test
Do not use deodorant, perfume, powders, or ointments under your arms or on your breasts on the day of the mammogram. These substances may hide a portion of the images or produce an artifact that can falsely look like an abnormality. Remove all jewelry from your neck and chest area.
Tell your provider and the x-ray technologist if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, or if you've had a breast biopsy.
How the Test will Feel
The compressor surfaces may feel cold. When the breast is pressed down, you may feel some brief pain or discomfort. This needs to be done to get good quality images.
Why the Test is Performed
When and how often to have a screening mammogram is a choice you must make. Different expert groups do not fully agree on the best timing for this test.
Before having a mammogram, talk to your provider about the pros and cons of having the test. Ask about:
- Your risk for breast cancer
- Whether screening decreases your chance of dying from breast cancer
- Whether there is any harm from breast cancer screening, such as side effects from testing or overtreatment of cancer when it's discovered
Mammography is performed to screen women to detect early breast cancer when it is more likely to be cured. The recommendations of different expert organizations can differ.
- Mammography is generally recommended for all women starting at age 40, repeated every 1 to 2 years.
- Women with a family history of breast cancer should work with their provider to assess their risk of breast cancer. In some situations, additional testing may be considered.
Mammograms work best at finding breast cancer in women ages 40 to 74. It is not clear how well mammograms work at finding cancer in women age 75 and older.
Mammography is also used to:
- Follow a woman who has had an abnormal mammogram.
- Evaluate a woman who has symptoms of a breast disease. These symptoms may include a lump, nipple discharge, breast pain, dimpling of the skin on the breast, changes of the nipple, or other findings.
Normal Results
Breast tissue that shows no signs of a mass or suspicious looking calcifications is considered normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Most abnormal findings on a screening mammogram turn out to be benign (not cancer) or nothing to worry about. New findings or changes must be further evaluated.
A radiology specialist (radiologist) may see the following types of findings on a mammogram:
- A well-outlined, smoothly marginated, rounded spot (this is more likely to be a noncancerous condition, such as a cyst)
- Irregular appearing masses or lumps
- Dense areas in the breast that can be breast cancer or hide breast cancer
- Calcifications, which are caused by tiny deposits of calcium in the breast tissue (most calcifications are not a sign of cancer)
At times, the following tests are also needed to further assess mammogram findings:
- Additional mammogram views, including magnification or compression views
- Breast ultrasound
- Breast MRI exam (less commonly done)
Comparing your current mammogram to your past mammograms helps the radiologist tell whether you had an abnormal finding in the past and whether it has changed.
When mammogram or ultrasound results look suspicious, a biopsy is done to test the tissue and see if it is cancerous. Types of biopsies include:
- Stereotactic (guided)
- Ultrasound (guided)
- Open (surgical)
Risks
The level of radiation is low and any risk from mammography is very low. If you are pregnant and need to have an abnormality checked, your belly area will be covered and protected by a lead apron.
Routine screening mammography is not done during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Alternative Names
Mammography; Breast cancer - mammography; Breast cancer - screening mammography; Breast lump - mammogram; Breast tomosynthesis; 3D mammography; 2D mammography; Diagnostic mammogram
References
Allweis TM, Grubstein A, Menes T. Breast cancer screening. In: Klimberg VS, Gradishar WJ, Bland KI, Korourian S, White J, Copeland EM, eds. Bland and Copeland's The Breast: Comprehensive Management of Benign and Malignant Diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 12.
American Cancer Society website. American Cancer Society recommendations for the early detection of breast cancer. www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/screening-tests-and-early-detection/american-cancer-society-recommendations-for-the-early-detection-of-breast-cancer.html. Revised December 19, 2023. Accessed January 27, 2025.
American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Age to initiate routine breast cancer screening. ACOG Clinical Practice Update. Obstet Gynecol. 2025;145(1):e40-e44. PMID: 39388713 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39388713/.
Henry NL, Shah PD, Haider I, Freer PE, Jagsi R, Sabel MS. Cancer of the breast. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 88.
National Cancer Institute website. Breast cancer screening (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/breast/hp/breast-screening-pdq. Updated October 9, 2024. Accessed January 27, 2025.
US Preventive Services Task Force; Nicholson WK, Silverstein M, et al. Screening for breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2024;331(22):1918-1930. PMID: 38687503 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38687503/.
Review Date 1/15/2025
Updated by: Kenneth Levin, MD, Private Practice specializing in Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Allentown, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.