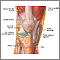
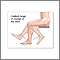
Limited range of motion is a term meaning that a joint or body part cannot move through its normal range of motion.
Considerations
Motion may be limited because of a problem within the joint, swelling of tissue around the joint, stiffness of the ligaments and muscles, or pain.
Causes
A sudden loss of range of motion may be due to:
- Dislocation of a joint
- Fracture of an elbow or other joint
- Infected joint (hip is most common in children)
- Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (in boys 4 to 10 years old)
- Nursemaid elbow, an injury to the elbow joint in young children
- Tearing of certain structures within the joint, such as the meniscus or cartilage
- Lose bodies which have become stuck in the joint
Loss of motion may occur if you damage the bones within a joint. This may happen if you have:
- Broken a joint bone in the past
- Frozen shoulder
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis (a specific form of arthritis)
Brain, nerve, or muscle disorders can damage the nerves, tendons, and muscles, and can cause loss of motion. Some of these disorders include:
- Cerebral palsy (group of disorders that involve brain and nervous system functions)
- Congenital torticollis (wry neck)
- Muscular dystrophy (group of inherited disorders that cause muscle weakness)
- Stroke or brain injury
- Volkmann contracture (deformity of the hand, fingers, and wrist caused by injury to the muscles of the forearm)
Home Care
Your health care provider may suggest exercises to increase muscle strength and flexibility.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have difficulty moving or extending a joint.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will examine you and ask about your medical history and symptoms.
You may need joint x-rays and spine x-rays. Lab tests may be done.
Physical therapy may be recommended.
References
Debski RE, Patel NK, Shearn JT. Basic concepts in biomechanics. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 2.
Magee DJ, Manske RC. Primary care assessment. Magee DJ, Manske RC, eds. Orthopedic Physical Assessment. 7th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2021:chap 17.
Review Date 8/27/2024
Updated by: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.