Summary
Good posture is about more than standing up straight so you can look your best. It is an important part of your long-term health. Making sure that you hold your body the right way, whether you are moving or still, can prevent pain, injuries, and other health problems.
What is posture?
Posture is how you hold your body. There are two types:
- Dynamic posture is how you hold yourself when you are moving, like when you are walking, running, or bending over to pick up something.
- Static posture is how you hold yourself when you are not moving, like when you are sitting, standing, or sleeping.
It is important to make sure that you have good dynamic and static posture.
The key to good posture is the position of your spine. Your spine has three natural curves - at your neck, mid back, and low back. Correct posture should maintain these curves, but not increase them. Your head should be above your shoulders, and the top of your shoulder should be over the hips.
How can posture affect my health?
Poor posture can be bad for your health. Slouching or slumping over can:
- Misalign your musculoskeletal system
- Wear away at your spine, making it more fragile and prone to injury
- Cause neck, shoulder, and back pain
- Decrease your flexibility
- Affect how well your joints move
- Affect your balance and increase your risk of falling
- Make it harder to digest your food
- Make it harder to breathe
How can I improve my posture in general?
- Be mindful of your posture during everyday activities, like watching television, washing dishes, or walking
- Stay active. Any kind of exercise may help improve your posture, but certain types of exercises can be especially helpful. They include yoga, tai chi, and other classes that focus on body awareness. It is also a good idea to do exercises that strengthen your core (muscles around your back, abdomen, and pelvis).
- Maintain a healthy weight. Extra weight can weaken your abdominal muscles, cause problems for your pelvis and spine, and contribute to low back pain. All of these can hurt your posture.
- Wear comfortable, low-heeled shoes. High heels, for example, can throw off your balance and force you to walk differently. This puts more stress on your muscles and harms your posture.
- Make sure work surfaces are at a comfortable height for you, whether you're sitting in front of a computer, making dinner, or eating a meal.
How can I improve my posture when sitting?
Many Americans spend a lot of their time sitting - either at work, at school, or at home. It is important to sit properly, and to take frequent breaks:
- Switch sitting positions often
- Take brief walks around your office or home
- Gently stretch your muscles every so often to help relieve muscle tension
- Don't cross your legs; keep your feet on the floor, with your ankles in front of your knees
- Make sure that your feet touch the floor, or if that's not possible, use a footrest
- Relax your shoulders; they should not be rounded or pulled backwards
- Keep your elbows in close to your body. They should be bent between 90 and 120 degrees.
- Make sure that your back is fully supported. Use a back pillow or other back support if your chair does not have a backrest that can support your lower back's curve.
- Make sure that your thighs and hips are supported. You should have a well-padded seat, and your thighs and hips should be parallel to the floor.


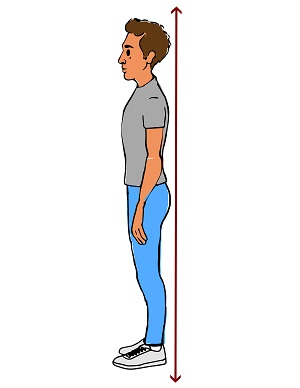
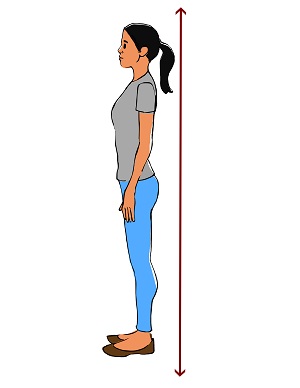
How can I improve my posture when standing?
- Stand up straight and tall
- Keep your shoulders back
- Pull your stomach in
- Put your weight mostly on the balls of your feet
- Keep your head level
- Let your arms hang down naturally at your sides
- Keep your feet about shoulder-width apart
With practice, you can improve your posture; you will look and feel better.
Learn More
- Axial Extension (Posture Exercise) (National Jewish Health)
-
Back Health
 (National Institutes of Health, Office of Research Services, Division of Occupational Health and Safety.)
(National Institutes of Health, Office of Research Services, Division of Occupational Health and Safety.)
- Back Safety: Poor Posture Hurts (Department of Veterans Affairs)
- Computer Workstations: Good Working Positions (Occupational Safety and Health Administration)
-
Getting It Straight: Improve Your Posture for Better Health
 (National Institutes of Health)
Also in Spanish
(National Institutes of Health)
Also in Spanish
- Neck pain (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
- Protecting Your Neck: Posture and Body Mechanics (Department of Veterans Affairs)
- Shoulder Blade Squeeze (Posture Exercise) (National Jewish Health)
- Taking care of your back at home (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
- Yoga for health (Medical Encyclopedia) Also in Spanish
Clinical Trials
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Posture and Health
 (National Institutes of Health)
(National Institutes of Health)
Journal Articles References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
- Article: Effects of unilateral neck muscle vibration on tilt direction and variability...
- Article: Head posture before and after the correction of unilateral functional posterior...
- Article: The effect of school-based functional training for physical fitness and postural...
- Guide to Good Posture -- see more articles


