Geneticists use maps to describe the location of a particular gene on a chromosome. One type of map uses the cytogenetic location to describe a gene’s position. The cytogenetic location is based on a distinctive pattern of bands created when chromosomes are stained with certain chemicals. Another type of map uses the molecular location, which is a precise description of a gene's position on a chromosome. The molecular location is based on the sequence of DNA building blocks (nucleotides) that make up the chromosome.
Cytogenetic location
Geneticists use a standardized way of describing a gene's cytogenetic location. In most cases, the location describes the position of a particular band on a stained chromosome:
17q12
It can also be written as a range of bands, if less is known about the exact location:
17q12-q21
The combination of numbers and letters provide a gene's “address” on a chromosome. This address is made up of several parts:
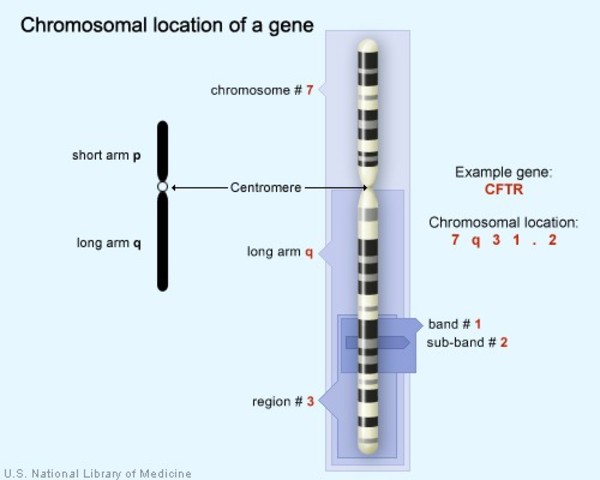
The chromosome on which the gene can be found. The first number or letter used to describe a gene's location represents the chromosome. Chromosomes 1 through 22 (the autosomes) are designated by their chromosome number. The sex chromosomes are designated by X or Y.
The arm of the chromosome. Each chromosome is divided into two sections (arms) based on the location of a narrowing (constriction) called the centromere. By convention, the shorter arm is called p, and the longer arm is called q. The chromosome arm is the second part of the gene's address. For example, 5q is the long arm of chromosome 5, and Xp is the short arm of the X chromosome.
The position of the gene on the p or q arm. The position of a gene is based on a distinctive pattern of light and dark bands that appear when the chromosome is stained in a certain way. The position is usually designated by two digits (representing a region and a band), which are sometimes followed by a decimal point and one or more additional digits (representing sub-bands within a light or dark area). The number indicating the gene position increases with distance from the centromere. For example: 14q21 represents position 21 on the long arm of chromosome 14. 14q21 is closer to the centromere than 14q22.
Sometimes, the abbreviations “cen” or “ter” are also used to describe a gene's cytogenetic location. “Cen” indicates that the gene is very close to the centromere. For example, 16pcen refers to the short arm of chromosome 16 near the centromere. “Ter” stands for terminus, which indicates that the gene is very close to the end of the p or q arm. For example, 14qter refers to the tip of the long arm, or the very end, of chromosome 14.
The CFTR gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 7 at position 7q31.2.
Molecular location
The Human Genome Project, an international research effort completed in 2003, determined the sequence of nucleotides for each human chromosome. This sequence information allows researchers to provide a more specific address than the cytogenetic location for many genes. A gene’s molecular address pinpoints the location of that gene in terms of nucleotides. It describes the gene’s precise position on a chromosome and indicates the size of the gene. Knowing the molecular location also allows researchers to determine exactly how far a gene is from other genes on the same chromosome.
Different groups of researchers often present slightly different values for a gene’s molecular location. Researchers interpret the sequence of the human genome using a variety of methods, which can result in small differences in a gene’s molecular address.
Topics in the How Genes Work chapter
The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Contact a health care provider if you have questions about your health.


