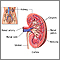
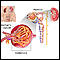
Dialysis treats end-stage kidney disease also called kidney failure. It removes waste from your blood when your kidneys can no longer do their job.
There are different types of kidney dialysis. This article focuses on hemodialysis.
What is Hemodialysis?
Your kidneys' main job is to remove toxins and extra fluid from your blood as well as to regulate some of the chemicals in your blood. If waste products build up in your body, it can be dangerous and even cause death.
Hemodialysis (and other types of dialysis) does some of the job of the kidneys when they stop working well.
Hemodialysis can:
- Remove extra salt, water, and waste products so they don't build up in your body
- Keep safe levels of minerals and vitamins in your body
- Help control blood pressure
- Help produce red blood cells
During hemodialysis, your blood passes through a tube into an artificial kidney or filter.
- The filter, called a dialyzer, is divided into 2 parts separated by a thin wall.
- As your blood passes through one part of the filter, special fluid in the other part draws out waste from your blood.
- Your blood then goes back into your body through a tube.
Your doctor will create an access where the tube attaches. Usually, an access will be in a blood vessel in your arm.
When to Start Dialysis
Kidney failure is the last stage of long-term chronic kidney disease. This is when your kidneys can no longer support your body's needs. Your health care provider will discuss dialysis with you before you need it. Usually, you will go on dialysis when you have only 10% to 15% of your kidney function left.
You also may need dialysis if your kidneys suddenly stop working due to acute renal failure.
Dialysis at a Treatment Center
Hemodialysis is most often done at a special dialysis center.
- You will have about 3 treatments a week.
- Treatment takes about 3 to 4 hours each time.
- You may feel tired for several hours after the dialysis.
At a treatment center, your providers will handle all your care. However, you do need to schedule your appointments and follow a strict dialysis diet.
Dialysis at Home
You may be able to have hemodialysis at home. You do not have to buy a machine. Medicare or your health insurance will pay for most or all of your treatment costs at home or in a center.
If you have dialysis at home, you can use one of two schedules:
- Shorter (2 to 3 hours) treatments done at least 5 to 7 days per week
- Longer, nightly treatments done 3 to 6 nights per week while you sleep
You also may be able to do a combination of daily and nighttime treatments.
Because you have treatment more often and it happens more slowly, home hemodialysis has some benefits:
- It helps keep your blood pressure lower. Many people no longer need blood pressure medicines.
- It does a better job of removing waste products.
- It's easier on your heart.
- You may have fewer symptoms from dialysis such as nausea, headaches, cramps, itching, and tiredness.
- You can more easily fit treatments into your schedule.
You can do the treatment yourself, or you can have someone help you. A dialysis nurse can train you and a caregiver on how to do home dialysis. Training can take a few weeks to a few months. Both you and your caregivers must learn to:
- Handle the equipment
- Place the needle into the access site
- Monitor the machine and your blood pressure during treatment
- Keep records
- Clean the machine
- Order supplies, which can be delivered to your home
Home dialysis is not for everyone. You will have a lot to learn and need to be responsible for your care. Some people feel more comfortable having a provider handle their treatment. Plus, not all centers offer home dialysis.
Home dialysis may be a good option if you want more independence and are able to learn to treat yourself. Talk with your provider. Together, you can decide what type of hemodialysis is right for you.
When to Call Your Doctor
Contact your provider if you notice:
- Bleeding from your vascular access site
- Signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, soreness, pain, warmth, or pus around the site
- A fever over 100.5°F (38.0°C)
- The arm where your catheter is placed swells and the hand on that side feels cold
- Your hand gets cold, numb, or weak
Also, contact your provider if any of the following symptoms are severe or last more than 2 days:
- Itching
- Trouble sleeping
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Drowsiness, confusion, or problems concentrating
Alternative Names
Artificial kidneys - hemodialysis; Dialysis; Renal replacement therapy - hemodialysis; End-stage renal disease - hemodialysis; Kidney failure - hemodialysis; Renal failure - hemodialysis; Chronic kidney disease - hemodialysis
References
Cohen D, Valeri AM. Treatment of irreversible renal failure. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 117.
Kotanko P, Kuhlmann MK, Chan C, Levin NW. Hemodialysis: principles and techniques. In: Johnson RJ, Floege J, Tonelli M, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 98.
Misra M. Hemodialysis and hemofiltration. In: Gilbert SJ, ed. National Kidney Foundation Primer on Kidney Diseases. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 56.
Yeun JY, Young B, Depner TA, Chin AA. Hemodialysis. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 63.
Review Date 3/31/2024
Updated by: Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.