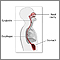
Eosinophilic esophagitis involves a buildup of a specific type of white blood cells, called eosinophils, in the lining of your esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach. The buildup of eosinophils that causes eosinophilic esophagitis is due to a reaction to foods or allergens.
Causes
The exact cause of eosinophilic esophagitis is not known. It is believed that an immune reaction to certain foods leads to a buildup of eosinophils. As a result, the lining of the esophagus becomes swollen and inflamed.
Most people with this disorder have a family or personal history of allergies or asthma. Triggers such as mold, pollen, and dust mites may also play a role.
Symptoms
Eosinophilic esophagitis can affect both children and adults.
Symptoms in children include:
- Problems feeding or eating
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Problems swallowing
- Food getting stuck in the esophagus
- Poor weight gain or weight loss, poor growth, and malnutrition
Symptoms in adults include:
- Food getting stuck when swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chest pain
- Heartburn
- Upper abdominal pain
- Backflow of undigested food (regurgitation)
- Reflux in the esophagus that does not get better with medicine
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will take a detailed history and perform a physical exam. This is done to check for food allergies and to rule out other conditions, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Tests that may be done include:
- Blood tests
- Allergy skin test
- Upper endoscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy)
- Biopsy of the lining of the esophagus
Eosinophilic esophagitis is diagnosed when a certain amount of eosinophils are seen under the microscope after an esophagus biopsy.
Treatment
There is no cure at this time. Treatment involves managing your diet and taking medicines.
If you test positive for food allergies, you may be told to avoid those foods. Or you may avoid all foods that are known to trigger this problem. Common foods that cause eosinophilic esophagitis include seafood, eggs, nuts, soy, wheat, and dairy. Allergy testing may discover specific foods to avoid, but is not always helpful. Talk to your provider about what foods to avoid.
Proton pump inhibitors can help control symptoms. They may also help treat inflammation of the esophagus.
Your provider may prescribe topical steroids taken orally or inhaled. You also may take oral steroids for a short time. Topical steroids don't have the same side effects as oral steroids. You must rinse your mouth after using topical steroids.
If you develop narrowing or strictures, a procedure to open up or dilate the area may be needed. This is done during an endoscopy.
New medicines have been approved to help with eosinophilic esophagitis. They may be used by mouth or injected.
You and your provider will work together to find a treatment plan that works best for you.
Support Groups
Support groups such as American Partnership for Eosinophilic Disorders can help you understand more about eosinophilic esophagitis. You can also learn ways to manage your condition and cope with the disease.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Eosinophilic esophagitis is long-term (chronic) disease that comes and goes over a person's lifetime.
Possible Complications
Possible complications may include:
- Narrowing of the esophagus (a stricture)
- Food getting stuck in the esophagus (common in both children and adults)
- Severe swelling and irritation of the esophagus
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis.
References
Bird JA. Food allergies. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 10.
Falk GW, Katzka DA. Diseases of the esophagus. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 124.
Hirano I, Chan ES, Rank MA, et al. on behalf of the AGA Institute Clinical Guidelines Committee and the Joint Task Force on Allergy-Immunology Practice Parameters. AGA Institute and the Joint Task Force on Allergy-Immunology Practice Parameters Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(6):1776-1786. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32359562/.
Khan S. Eosinophilic esophagitis, pill esophagitis, and infective esophagitis. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 370.
Review Date 6/11/2024
Updated by: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.