Overview
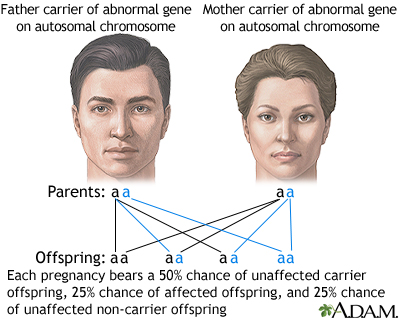
Autosomal recessive is one of several ways that a trait, disorder, or disease can be passed down through families. An autosomal recessive disorder means two copies of an abnormal gene must be present in order for the disease or trait to develop. For a child born to a couple who both carry the gene (but the parents themselves do not have signs of disease), the expected outcome for each pregnancy is: a 50% chance that the child is born with one normal and one abnormal gene (carrier, without disease), a 25% chance that the child is born with two normal genes (normal), and a 25% chance that the child is born with two abnormal genes (at risk for the disease). Note: These outcomes do not mean that the children will definitely be carriers or be severely affected.
Review Date 4/8/2025
Updated by: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


